1945 (Age 18-19)
Clayton served in the Coast Guard form 1944 - 1946More about V-E Day
May 08, 1945
V-E Day is celebrated in America and Britain
On this day in 1945, both Great Britain and the United States celebrate Victory in Europe Day. Cities in both nations, as well as formerly occupied cities in Western Europe, put out flags and banners, rejoicing in the defeat of the Nazi war machine.
The eighth of May spelled the day when German troops throughout Europe finally laid down their arms: In Prague, Germans surrendered to their Soviet antagonists, after the latter had lost more than 8,000 soldiers, and the Germans considerably more; in Copenhagen and Oslo; at Karlshorst, near Berlin; in northern Latvia; on the Channel Island of Sark—the German surrender was realized in a final cease-fire. More surrender documents were signed in Berlin and in eastern Germany.
The main concern of many German soldiers was to elude the grasp of Soviet forces, to keep from being taken prisoner. About 1 million Germans attempted a mass exodus to the West when the fighting in Czechoslovakia ended, but were stopped by the Russians and taken captive. The Russians took approximately 2 million prisoners in the period just before and after the German surrender.
Meanwhile, more than 13,000 British POWs were released and sent back to Great Britain.
Pockets of German-Soviet confrontation would continue into the next day. On May 9, the Soviets would lose 600 more soldiers in Silesia before the Germans finally surrendered. Consequently, V-E Day was not celebrated until the ninth in Moscow, with a radio broadcast salute from Stalin himself: “The age-long struggle of the Slav nations… has ended in victory. Your courage has defeated the Nazis. The war is over.”
More about V-J Day
August 14, 1945
On August 14, 1945, it was announced that Japan had surrendered unconditionally to the Allies, effectively ending World War II. Since then, both August 14 and August 15 have been known as “Victoryover Japan Day,” or simply “V-J Day.” The term has also been used for September 2, 1945, when Japan’s formal surrender took place aboard the U.S.S. Missouri, anchored in Tokyo Bay. Coming several months after the surrender of Nazi Germany, Japan’s capitulation in the Pacific brought six years of hostilities to a final and highly anticipated close.
From Pearl Harbor to Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Japan’s devastating surprise aerial attack on the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor on Oahu, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941, capped a decade of deteriorating relations between Japan and the United States and led to an immediate U.S. declaration of war the following day. Japan’s ally Germany, led by Adolf Hitler, then declared war on the United States, turning the war raging in Europe into a truly global conflict. Over the next three years, superior technology and productivity allowed the Allies to wage an increasingly one-sided war against Japan in the Pacific, inflicting enormous casualties while suffering relatively few. By 1945, in an attempt to break Japanese resistance before a land invasion became necessary, the Allies were consistently bombarding Japan from air and sea, dropping some 100,000 tons of explosives on more than 60 Japanese cities and towns between March and July 1945 alone.
The Potsdam Declaration, issued by Allied leaders on July 26, 1945, called on Japan to surrender; if it did, it was promised a peaceful government according to “the freely expressed will of the Japanese people.” If it did not, it would face “prompt and utter destruction.” The embattled Japanese government in Tokyo refused to surrender, and on August 6 the American B-29 plane Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on the city of Hiroshima, killing more than 70,000 people and destroying a 5-square-mile expanse of the city. Three days later, the United States dropped a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki, killing another 40,000. The following day, the Japanese government issued a statement accepting the terms of the Potsdam Declaration. In a radio address in the early afternoon of August 15 (August 14 in the United States), Emperor Hirohito urged his people to accept the surrender, blaming the use of the “new and most cruel bomb” on Hiroshima and Nagasaki for the country’s defeat. “Should we continue to fight,” Hirohito declared, “it would not only result in the ultimate collapse and obliteration of the Japanese nation but would also lead to the total extinction of human civilization.”
Reaction to Japanese Surrender
In Washington on August 14, President Harry S. Truman announced news of Japan’s surrender in a press conference at the White House: “This is the day we have been waiting for since Pearl Harbor. This is the day when Fascism finally dies, as we always knew it would.” Jubilant Americans declared August 14 “Victory over Japan Day,” or “V-J Day.” (May 8, 1945–when the Allies accepted Nazi Germany’s official surrender–had previously been dubbed “Victory in Europe Day,” or “V-E Day.”)
Images from V-J Day celebrations around the United States and the world reflected the overwhelming sense of relief and exhilaration felt by citizens of Allied nations at the end of the long and bloody conflict. In one particularly iconic photo taken by Alfred Eisenstaedt for Life magazine, a uniformed sailor passionately kisses a nurse in the midst of a crowd of people celebrating in New York City’s Times Square. On September 2, Allied supreme commander General Douglas MacArthur, along with the Japanese foreign minister, Mamoru Shigemitsu, and the chief of staff of the Japanese army, Yoshijiro Umezu, signed the official Japanese surrender aboard the U.S. Navy battleship Missouri, effectively ending World War II.
Memorable Pictures and Documents
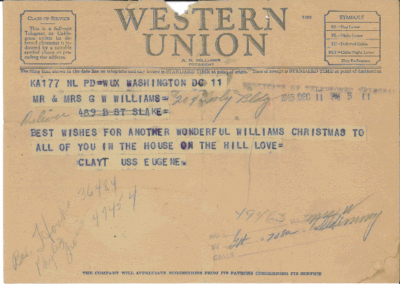
from Clayton Ray William's Coast Guard Service in WWII:More Pictures with Mary Lois Sharp:
VE Day and VJ Day